
When the medicine's effects wear off, some children's hyperactive behaviors may increase for a short while. Side effects include trouble sleeping, decreased appetite, stomach ache, headache, and nervousness. Psychostimulant medicines can cause side effects. The behaviors and physical symptoms the family should watch for and report The medicine dose, how often it should be given, and frequency of follow-up visits.

If these standards are met, then medicine education will be done. Children with symptoms of substance abuse will be referred for evaluation and treatment for addiction before ADHD medicines are prescribed.
#Medication for adhd full
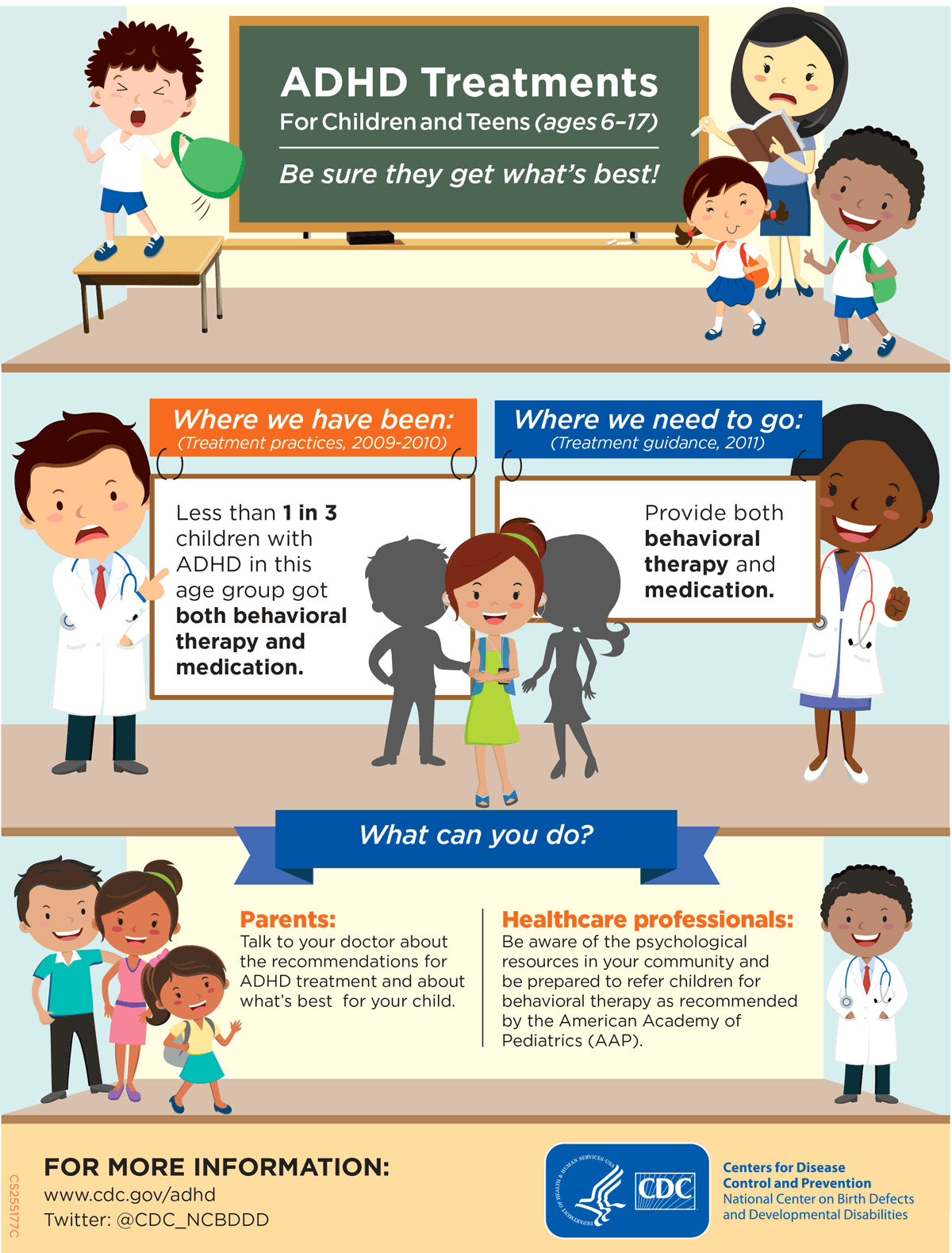
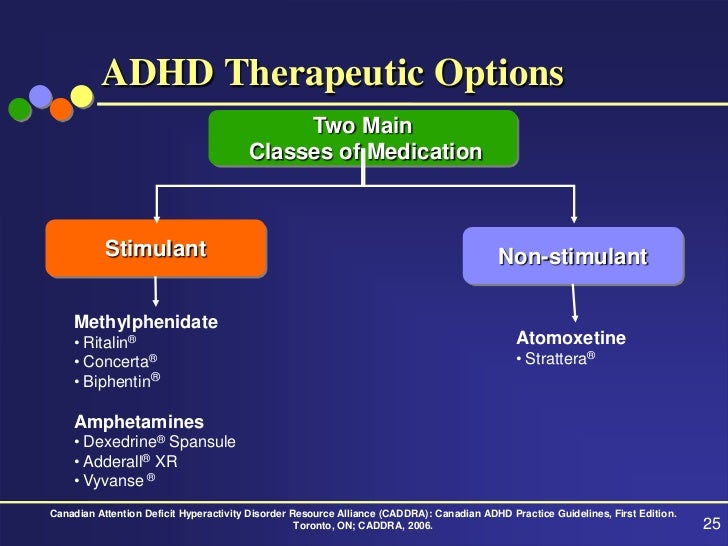
These can include:Ī full heart-focused health history, family history, and physical examīaseline height, weight, blood pressure, and heart rateīaseline information for common side effects linked to ADHD medicines (such as belly pain, sleep patterns, and appetite) This is done after evaluating your child's symptoms, age and health, and your preference.īefore ADHD medicine is started, your child will be checked to be sure they meet certain standards for treatment. Your healthcare provider will determine your child's need for medicine and select the appropriate medicine. These include:Īntidepressant medicines such as bupropion, desipramine, and imipramine Sometimes nonstimulant medicines may be used to treat ADHD in children. They work for up to 9 hours and need to be taken only once a day. Some psychostimulants on the market are designed to be longer acting. They are then quickly flushed from the body. These include dextroamphetamine, a mixture of amphetamine salts, and atomoxetine. Healthcare providers also prescribe other psychostimulants. Healthcare providers often prescribe psychostimulants, such as methylphenidate. These medicines help balance chemicals in your child's brain that help to control their behavior and focus their attention. Children who have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are often given medicine as part of their treatment plan.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
